Assessment and management of proximal humerus fractures
by James Donaldson
Scenario: called to A&E to assess a 68 year old woman who fell from a height onto her shoulder.
History
Age – often elderly, in the young consider higher energy trauma
Occupation and handedness – useful for deciding treatment, rehab protocol, compliance
Time/date of injury
Past medical/surgical history
Medication/drugs and allergies
Last ate/drank (for timing of emergency surgery if needed)
Radiographs
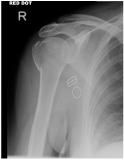
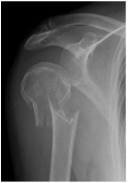
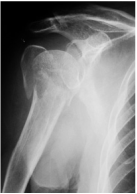
3 radiographs are mandatory for all shoulder injuries:
History
Age – often elderly, in the young consider higher energy trauma
Occupation and handedness – useful for deciding treatment, rehab protocol, compliance
Time/date of injury
Past medical/surgical history
Medication/drugs and allergies
Last ate/drank (for timing of emergency surgery if needed)
Radiographs
3 radiographs are mandatory for all shoulder injuries:
- AP, Scapula Y and axillary radiographs
- Additional views +/- CT can be ordered by treating surgeon if needed
- Assess bony contours and presence of fractures / dislocations
Evaluation
Acute pain after the injury
Loss of function and range of movement
Swelling, bruising and deformity
Associated injuries
Chest, lung, head, spine, scapula. Involve trauma team if necessary
Neurovascular exam
Anatomy
Typically the shoulder is divided into 4 anatomical parts:
Acute pain after the injury
Loss of function and range of movement
Swelling, bruising and deformity
Associated injuries
Chest, lung, head, spine, scapula. Involve trauma team if necessary
Neurovascular exam
- Especially axillary nerve palsy (up to 45%)
- Brachial plexus - refer urgently to specialist centre (BOAST guidelines)
- Arterial injury - emergency vascular consultation if suspected
Anatomy
Typically the shoulder is divided into 4 anatomical parts:
- Greater tuberosity
- Lesser tuberosity
- Articular surface / head
- Shaft of humerus
Initial treatment
Analgesia, collar and cuff
Collar and cuff and 1 week fracture clinic follow up if non-operative treatment is indicated
Admit (and inform senior) if neurovascular injury or associated dislocation or if operative treatment is indicated
85% of fractures are treated non-operatively
Decision to operate depends on many factors including:
Analgesia, collar and cuff
Collar and cuff and 1 week fracture clinic follow up if non-operative treatment is indicated
Admit (and inform senior) if neurovascular injury or associated dislocation or if operative treatment is indicated
85% of fractures are treated non-operatively
Decision to operate depends on many factors including:
- age
- fracture type and displacement
- bone quality
- handedness
- medical conditions and concurrent injuries
|
Management
Decision dependent on degree of displacement. Fractures classified by displacement rather than number of fracture fragments. If a fragment is undisplaced, it is not defined as a part. One part fracture Typically undisplaced can involve 1-4 fragments but none are displaced. Surgical neck #. Commonest type. Non-operative management. Anatomical neck #. ORIF in young. ORIF or hemi-arthroplasty in elderly if comminuted Two part fracture Involves one displaced fragment ORIF if significantly displaced or angulated ORIF greater tuberosity if >5mm displaced Three or four part fractures Involve two or more displaced fragments ORIF or hemi-arthroplasty in elderly |